- understanding-feline-gi-disease-advance
- early-warning-signs-of-gi-disease-in-cats
- how-advanced-gi-disorders-affect-feline-health
- real-case-stories-of-cats-with-gi-disease
- diagnosing-advanced-feline-gi-disease
- treatment-options-for-advanced-gi-conditions
- home-care-tips-for-cats-with-gi-disease
- when-to-seek-specialized-veterinary-support
Understanding Feline GI Disease Advance
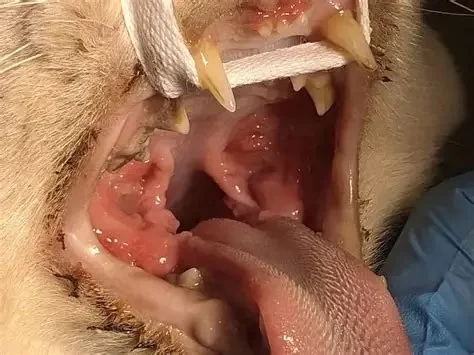
Feline gastrointestinal (GI) disease can range from mild digestive upset to severe, advanced conditions that require ongoing management. When a cat reaches the stage of feline GI disease advance, symptoms become more pronounced, chronic, and often more complex to treat. This stage typically includes inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), chronic vomiting disorders, pancreatitis-linked GI problems, or long-term dietary intolerances that have gone untreated.
Owners often describe this stage as “something just feels off,” long before the more visible symptoms appear. Many of the cats treated at facilities like Hidden Brook Veterinary show early behavioral changes that later reveal severe GI complications. Understanding these early patterns is essential for timely intervention.
Early Warning Signs of GI Disease in Cats
While some symptoms appear subtle at first, advanced GI disease typically develops over months. Recognizing early signals can prevent complications.
1. Chronic Vomiting or Regurgitation
An occasional hairball isn’t unusual, but vomiting several times a week is often the first indicator of a deeper issue. Cats experiencing GI disease advance may vomit undigested food, foam, or bile.
2. Persistent Diarrhea or Loose Stools
Chronic diarrhea is one of the strongest red flags. Textures may vary from watery to mucous-coated, depending on the severity and underlying cause.
3. Weight Loss Despite Eating Normally
This occurs when the digestive tract can no longer absorb nutrients properly, a hallmark of advanced GI disorders.
4. Loss of Appetite or Avoidance of Certain Foods
Cats may refuse their usual meals or show interest in food but walk away after sniffing. This behavior often signals nausea or stomach sensitivity.
5. Behavioral Shifts
Withdrawn behavior, irritability, hiding, or reduced grooming can indicate discomfort. Owners who notice these clues early often prevent the disease from progressing further.
How Advanced GI Disorders Affect Feline Health
As GI disease becomes advanced, the body struggles to maintain normal function. Chronic digestive distress affects a cat’s hydration, metabolism, immune system, and energy levels.
1. Compromised Nutrient Absorption
Cats with advanced GI issues can develop vitamin deficiencies, low muscle mass, and weakened immunity due to poor absorption.
2. Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance
Vomiting and diarrhea make it difficult for cats to retain fluids, creating dangerous imbalances that can lead to organ stress.
3. Pain and Inflammation
Inflamed tissue in the stomach and intestines causes ongoing discomfort, making daily activities challenging for affected cats.
Real Case Stories of Cats with GI Disease
One memorable case came from a family whose senior tabby, Milo, began vomiting every other day. At first, they believed it was hairballs, but the episodes grew more frequent. When Milo refused his favorite canned chicken dinner—a food he adored for nearly a decade—they knew something was wrong.
After testing, veterinarians discovered advanced inflammatory bowel disease. With dietary therapy, supportive medications, and ongoing monitoring, Milo slowly regained weight and energy. His story mirrors the experiences of many cats diagnosed at advanced stages, showing how critical early detection can be.
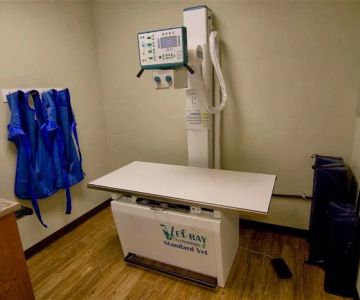
Diagnosing Advanced Feline GI Disease
Veterinary diagnosis typically involves multiple steps because GI disease can mimic other feline illnesses. Facilities like Hidden Brook Veterinary often follow a structured diagnostic path to pinpoint exact causes.
1. Blood Work and Chemistry Panels
These tests identify inflammation markers, organ strain, anemia, and electrolyte imbalances.
2. Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasounds help veterinarians visualize thickened intestinal walls, enlarged lymph nodes, or pancreatic irregularities.
3. Fecal Testing
To rule out parasites, infections, and bacterial overgrowth, fecal tests are essential.
4. Food Trials
Elimination diets reveal whether a cat’s symptoms are triggered by specific ingredients.
5. Biopsies for Definitive Diagnosis
In advanced cases, intestinal biopsies provide clear confirmation of chronic inflammatory disease or other GI disorders.
Treatment Options for Advanced GI Conditions
Treatment varies by diagnosis but often includes a combination of dietary adjustments, medications, and supportive therapies.
1. Prescription Diets
Hydrolyzed protein diets or limited-ingredient formulas help reduce inflammation and digestive reactions.
2. Anti-Inflammatory and Immune-Modulating Drugs
Medications such as corticosteroids or specific immune-regulating drugs may be required to control inflammation.
3. Probiotics and Digestive Enzymes
These support gut flora and help cats process food more effectively.
4. Hydration Support
Subcutaneous fluids may be recommended for cats experiencing dehydration from chronic symptoms.
5. Long-Term Monitoring
Advanced GI disease requires consistent follow-ups to ensure treatments continue working and symptoms remain controlled.
Home Care Tips for Cats With GI Disease
At-home management plays a huge role in long-term comfort and recovery.
1. Maintain a Consistent Feeding Schedule
Smaller, more frequent meals reduce stress on the digestive system.
2. Avoid Sudden Diet Changes
Any switch should be gradual, typically over one to two weeks.
3. Keep a Symptom Journal
Tracking vomiting episodes, stool changes, or appetite shifts helps veterinarians adjust treatment plans.
4. Provide a Calm Environment
Stress worsens GI symptoms, so minimizing noise and changes in routine is helpful.
When to Seek Specialized Veterinary Support
If your cat exhibits persistent digestive distress, weight loss, or behavioral changes, advanced veterinary care is crucial. Specialized support from experts such as those at Hidden Brook Veterinary can make all the difference in diagnosing complex GI issues and creating a treatment plan tailored to your cat’s needs.
With early recognition and targeted treatment, many cats with advanced GI disease regain comfort and enjoy a high quality of life. Monitoring symptoms, staying proactive, and seeking professional help as soon as concerns arise are the most important steps an owner can take.