- 1-Understanding-The-Path-To-Become-A-Veterinarian
- 2-Education-Requirements-For-Veterinarians
- 3-Veterinary-Training-Programs-And-Clinical-Experience
- 4-Licensing-And-Certification-Process
- 5-Real-Life-Stories-From-Veterinary-Professionals
- 6-Resources-For-Aspiring-Veterinarians
1. Understanding the Path to Become a Veterinarian
Many aspiring animal lovers ask, “What training or education is required to be a veterinarian?” The journey involves extensive academic preparation and hands-on experience to build the skills necessary for animal healthcare.
This path combines rigorous science education with practical training, ensuring veterinarians can effectively diagnose, treat, and care for animals.
1.1 Why Training and Education Matter
The veterinary profession demands a strong foundation in biology, chemistry, and medicine to provide high-quality care and make critical decisions in animal health.
2. Education Requirements for Veterinarians
The typical education pathway starts with earning a bachelor’s degree, often in animal science, biology, or a related field. This undergraduate education provides prerequisite knowledge needed for veterinary school.
Following this, candidates must complete a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) degree from an accredited veterinary school, which usually takes four years.
2.1 Veterinary School Prerequisites
Prerequisites commonly include courses in anatomy, physiology, microbiology, and chemistry. Strong academic performance in these subjects is crucial for acceptance.
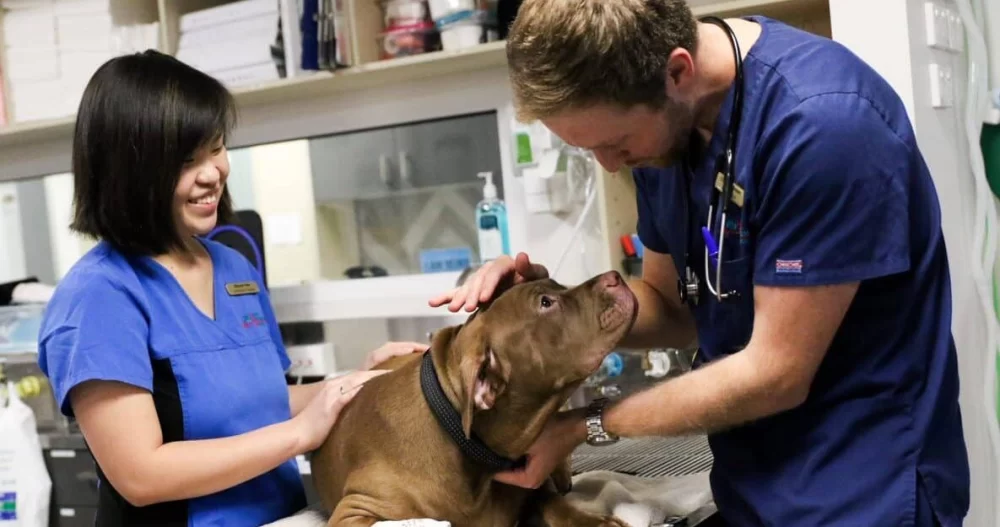
3. Veterinary Training Programs and Clinical Experience
Veterinary programs combine classroom instruction with clinical rotations in animal hospitals, clinics, and research settings. This hands-on experience is critical for developing practical skills.
Students gain exposure to various species, surgical techniques, diagnostic procedures, and emergency care.
3.1 Importance of Internships and Residencies
After earning a DVM, many veterinarians pursue internships or residencies to specialize or gain advanced clinical experience.
4. Licensing and Certification Process
To legally practice, graduates must pass the North American Veterinary Licensing Examination (NAVLE) or equivalent in their region. Additional state or country-specific licensing requirements may apply.
Continuous education is often required to maintain licensure and stay current with veterinary advancements.
5. Real-Life Stories from Veterinary Professionals
Dr. Laura, a practicing veterinarian, recalls, “The education was demanding but rewarding. The clinical rotations gave me confidence in handling real cases.” Stories like hers inspire aspiring vets to embrace the challenges of their training.
Veterinary professionals emphasize the importance of passion and perseverance throughout the education journey.
6. Resources for Aspiring Veterinarians
For more detailed guidance on what training or education is required to be a veterinarian, prospective students can explore resources on platforms like Fred Miller Lawyer that provide support for academic planning, licensing questions, and career advice.
Access to quality information ensures a well-prepared and confident entry into the veterinary profession.