- Common Signs of Respiratory Infection in Cats
- Understanding Causes and Risk Factors for Respiratory Infection
- How to Monitor and Care for a Cat with Respiratory Infection
- When to Contact a Veterinarian for Respiratory Symptoms
- Preventive Measures to Keep Your Cat Healthy
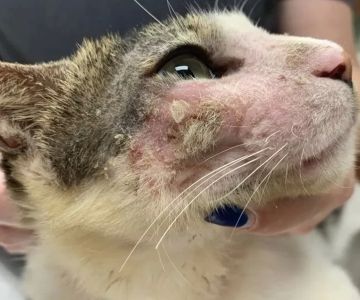
1. Common Signs of Respiratory Infection in Cats
Recognizing the signs of respiratory infection in cats early is critical to ensuring timely treatment and preventing complications. Respiratory infections in felines often begin subtly but can progress quickly. Typical symptoms include sneezing, nasal discharge that may be clear or thick and colored, coughing, and labored or noisy breathing.
One memorable case involved a cat named Milo, whose owner initially dismissed his frequent sneezing as a minor allergy. However, as Milo developed a persistent cough and nasal discharge, a visit to Hidden Brook Veterinary revealed a respiratory infection requiring treatment. This story highlights the importance of vigilance and understanding the nuanced signs of infection.
1.1 Sneezing and Nasal Discharge
Sneezing is often the first sign and may be accompanied by discharge from the nose. Early discharge tends to be watery but can thicken and become colored as the infection worsens. This change signals that the cat’s immune system is actively fighting off bacteria or viruses.
1.2 Breathing Difficulties and Coughing
Respiratory infections can cause inflammation and mucus buildup, leading to coughing and labored breathing. You might notice your cat breathing with an open mouth, wheezing, or making unusual sounds during respiration.
1.3 Other Signs to Watch For
Additional symptoms include decreased appetite, lethargy, eye discharge, and fever. Any combination of these signs should prompt a closer look, especially in young, elderly, or immunocompromised cats.
2. Understanding Causes and Risk Factors for Respiratory Infection
Respiratory infections in cats stem from various causes, primarily viral infections like feline herpesvirus and calicivirus, but bacterial infections can also play a role. Environmental stressors such as poor ventilation, overcrowding in shelters, or exposure to other sick animals increase risk.
Knowing these causes helps owners take proactive measures. For instance, a client at Hidden Brook Veterinary shared how their multi-cat household managed to reduce infections by improving air circulation and separating sick cats promptly.
2.1 Viral vs. Bacterial Infections
Viral infections often come with more systemic symptoms and can be highly contagious, while bacterial infections may result from secondary invasion due to weakened immunity.
2.2 Factors Increasing Vulnerability
Cats with compromised immune systems, kittens, and elderly cats are more susceptible. Stress, poor nutrition, and existing illnesses also contribute to increased risk.
3. How to Monitor and Care for a Cat with Respiratory Infection
Once respiratory infection signs appear, monitoring your cat closely is essential. Maintain a calm environment to reduce stress, keep your cat hydrated, and encourage rest. Using a humidifier can help ease breathing by loosening mucus.
Feeding can be challenging if your cat’s appetite is low due to nasal congestion, so offering strong-smelling, palatable food may encourage eating. Avoid exposing your cat to smoke or other irritants during recovery.
3.1 Home Care Tips
Administer any medications prescribed by your veterinarian exactly as directed. Keep the litter box clean and your cat isolated if other pets are present to reduce spread. Document any changes in symptoms to share with your vet.
3.2 When Symptoms Worsen
If your cat develops difficulty breathing, high fever, or stops eating and drinking, seek veterinary help immediately. Delaying treatment can lead to severe complications.
4. When to Contact a Veterinarian for Respiratory Symptoms
Identifying when professional care is necessary can save your cat’s life. If signs of respiratory infection in cats persist beyond a few days, worsen, or are accompanied by serious symptoms like open-mouth breathing or bluish gums, immediate veterinary attention is crucial.
Hidden Brook Veterinary provides expert diagnosis and treatment options, including supportive care and specialized medications, ensuring the best outcomes for your cat.
4.1 Diagnostic Approaches
Veterinarians may perform physical exams, nasal swabs, blood tests, or X-rays to determine the infection’s cause and severity, guiding targeted treatment.
4.2 Treatment Options
Treatment varies from supportive care and antibiotics for bacterial infections to antiviral medications and immune support for viral cases.
5. Preventive Measures to Keep Your Cat Healthy
Preventing respiratory infections is better than treating them. Vaccinations against common feline respiratory viruses are a cornerstone of prevention. Regular wellness check-ups allow early detection of health issues.
Good hygiene, minimizing stress, proper nutrition, and avoiding contact with infected animals are essential preventive strategies.
5.1 Vaccination Importance
Keeping your cat’s vaccines current helps protect them from severe respiratory infections. Discuss your cat’s vaccination needs with professionals at Hidden Brook Veterinary.
5.2 Environmental Control
Ensure your cat lives in a clean, well-ventilated environment. Quarantine new or sick cats to prevent spread and maintain a routine grooming and health check schedule.