- 1-Signs-of-Respiratory-Infection-in-Cats
- 2-Understanding-Respiratory-Infections-in-Cats
- 3-Common-Causes-of-Respiratory-Infections-in-Cats
- 4-Detailed-Explanation-of-Symptoms
- 5-Case-Studies-and-Real-Life-Examples
- 6-When-to-See-a-Veterinarian
- 7-Prevention-and-Care-for-Respiratory-Health
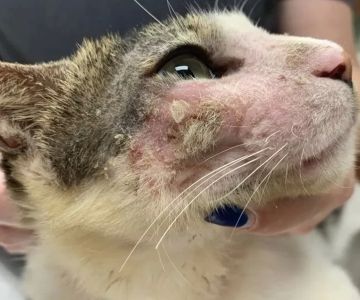
1. Recognizing Signs of Respiratory Infection in Cats
Cats are beloved companions, but their health can sometimes be delicate, especially when it comes to respiratory infections. Spotting the signs of respiratory infection in cats early is critical to ensure timely treatment and avoid complications. Common indicators include sneezing, coughing, nasal discharge, and difficulty breathing. These signs may seem mild at first but can quickly escalate, affecting your cat’s overall wellbeing. Understanding these symptoms allows cat owners to act swiftly, ensuring their feline friends receive the care they need before the infection worsens.
It's important to note that respiratory infections in cats can manifest subtly, often resembling a mild cold. However, because cats can hide illness, careful observation is necessary. If your cat shows lethargy or decreased appetite alongside respiratory symptoms, these could be signs of a more serious issue.
2. Understanding Respiratory Infections in Cats
Respiratory infections in cats generally affect the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, throat, and sinuses. These infections are commonly caused by viruses or bacteria. The feline herpesvirus and calicivirus are among the most frequent viral culprits, while bacteria such as Bordetella bronchiseptica can also play a role. Understanding the nature of these infections helps in tailoring effective treatments.
These infections are highly contagious among cats, especially in multi-cat households or shelters. The viruses can spread through sneezes, shared food bowls, or even grooming. Recognizing this helps owners implement proper hygiene and isolation practices to protect other pets.
3. Common Causes of Respiratory Infection in Cats
Several factors contribute to the development of respiratory infections in cats. Aside from viral and bacterial infections, environmental stressors like poor ventilation, dusty surroundings, or exposure to cigarette smoke can weaken a cat’s immune system, making them more susceptible. Additionally, young kittens, older cats, and those with compromised immune systems are at higher risk.
An interesting example is how shelter cats frequently face respiratory infections due to crowded and stressful conditions, illustrating the impact of environment on feline respiratory health.
4. Detailed Explanation of Symptoms
The symptoms of respiratory infection in cats vary but generally include:
- Sneezing: Frequent and forceful sneezing is often an early sign.
- Nasal Discharge: This can range from clear to thick and colored mucus.
- Coughing and Gagging: These indicate irritation or deeper airway involvement.
- Conjunctivitis: Red, swollen eyes with discharge often accompany infections.
- Loss of Appetite and Lethargy: These systemic signs show the cat is feeling unwell.
- Labored Breathing: This is a more serious symptom requiring immediate veterinary care.
Each symptom's severity can indicate how far the infection has progressed and whether complications like pneumonia are developing.
5. Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
Take the case of Luna, a 3-year-old indoor cat whose owner noticed she started sneezing excessively after a visit to the groomer. Initially, the symptoms seemed mild, but within days Luna developed nasal discharge and became less active. After a visit to Hidden Brook Veterinary, Luna was diagnosed with a viral respiratory infection and given supportive care including fluids and medication. Early intervention helped Luna recover fully within two weeks.
Another example involved Max, a shelter cat who presented with coughing and labored breathing. Max’s infection had progressed to pneumonia, requiring intensive veterinary treatment. This case underscores the importance of recognizing and acting on signs early to prevent serious outcomes.
6. When to See a Veterinarian
It is crucial for cat owners to know when to seek professional help. If your cat exhibits persistent sneezing lasting more than a few days, thick nasal discharge, difficulty breathing, or shows signs of lethargy and loss of appetite, a visit to the veterinarian should be scheduled immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Veterinary professionals at clinics like Hidden Brook Veterinary can provide thorough examinations, diagnostics such as blood tests or x-rays, and tailored treatment plans. They also advise on supportive care at home, which is essential for recovery.
7. Prevention and Care for Respiratory Health
Preventing respiratory infections in cats involves a combination of good hygiene, vaccination, and minimizing stress. Vaccines are available against common viral causes like feline herpesvirus and calicivirus, significantly reducing the risk of severe illness. Regular cleaning of litter boxes, food areas, and bedding helps reduce pathogen exposure.
Environmental factors also play a role — maintaining clean air, avoiding smoke, and ensuring proper ventilation all support respiratory health. Additionally, providing a stress-free environment boosts your cat’s immune system.
For cat owners looking for products or professional advice on managing or preventing respiratory infections, Hidden Brook Veterinary offers trusted recommendations tailored to your cat’s specific needs.