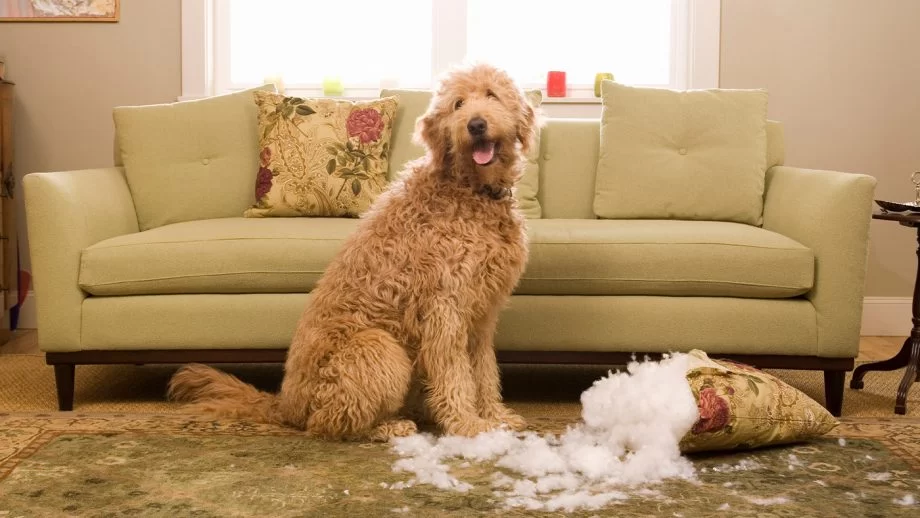
- Understanding Why Dogs Chew Furniture
- Identifying Common Triggers Behind Furniture Chewing
- Strategies to Prevent Furniture Chewing
- Training Techniques to Stop Chewing Behavior
- Using Environmental Management to Protect Furniture
- Professional Help and Products to Assist
1. Understanding Why Dogs Chew Furniture
Chewing is a natural behavior for dogs. Puppies use chewing as a way to relieve the discomfort of teething, while adult dogs may chew to alleviate boredom, stress, or anxiety. However, when dogs chew on furniture, it quickly becomes a frustrating problem for pet owners.
Dogs explore the world through their mouths, and furniture often presents an accessible target. In many cases, dogs may also chew on furniture due to separation anxiety or lack of sufficient mental and physical stimulation. Recognizing the root cause behind your dog’s furniture chewing is the first critical step in addressing the issue effectively.

1946 S Christopher Columbus Blvd, Philadelphia, PA 19148, USA
See Details1.1 The Role of Teething and Age
Young puppies experience intense discomfort during teething and instinctively chew to soothe their gums. Older dogs might chew out of habit or stress. Therefore, what starts as a puppy’s natural behavior can develop into a persistent problem if not addressed early.
1.2 Emotional and Environmental Factors
Stressors such as changes in the household, long periods of isolation, or insufficient exercise can increase destructive chewing. Some dogs also chew furniture as a way to get their owner's attention, especially if previous attempts have resulted in interaction, even if negative.
2. Identifying Common Triggers Behind Furniture Chewing
To stop dogs from chewing on furniture, understanding specific triggers is essential. Different dogs chew for different reasons, so identifying these helps tailor an effective approach.
2.1 Boredom and Lack of Exercise
Dogs left alone for extended periods without adequate physical activity or mental challenges tend to seek stimulation through chewing. A dog confined indoors without enrichment is more likely to target furniture out of sheer boredom.
2.2 Anxiety and Separation Stress
Dogs experiencing separation anxiety might chew to cope with their distress. This type of chewing is usually accompanied by other anxiety-related behaviors, such as whining, pacing, or excessive barking.
2.3 Inadequate Training or Reinforcement
Some dogs never learn appropriate chewing behaviors. Without clear boundaries and consistent training, dogs may not understand which items are off-limits. Additionally, unintentional reinforcement, such as giving attention when a dog is caught chewing, can worsen the behavior.
3. Strategies to Prevent Furniture Chewing
Preventing furniture chewing involves proactive management and training to redirect your dog’s natural chewing urges toward appropriate items.
3.1 Provide Suitable Chew Toys
Offering a variety of safe and engaging chew toys can satisfy your dog’s need to chew. Rotate toys regularly to maintain interest and encourage your dog to focus on them instead of furniture.
3.2 Increase Physical and Mental Exercise
Daily walks, playtime, and interactive games help burn off excess energy that might otherwise be channeled into destructive chewing. Puzzle feeders and obedience training sessions also provide mental stimulation that reduces boredom.
3.3 Use Deterrent Sprays and Barriers
Applying safe, bitter-tasting sprays on furniture can discourage chewing. Physical barriers, such as baby gates or furniture covers, can also prevent access and protect prized possessions.
4. Training Techniques to Stop Chewing Behavior
Behavioral training is key to teaching your dog what is acceptable to chew and what is not. Consistency and positive reinforcement form the foundation of successful training.
4.1 Redirect and Reward
When you catch your dog chewing furniture, calmly redirect their attention to an approved chew toy and reward them when they engage with it. Over time, your dog learns to associate chewing with positive outcomes on the right objects.
4.2 Teach Basic Commands
Commands like "leave it" and "no" can be invaluable tools to stop unwanted chewing instantly. Training sessions should be frequent and short to reinforce these commands effectively.
4.3 Avoid Punishment
Harsh punishments can increase anxiety and worsen destructive behavior. Instead, use gentle correction and reward-based techniques to encourage desired behavior.
5. Using Environmental Management to Protect Furniture
Sometimes, managing your dog’s environment is the most practical way to prevent chewing damage, especially during training.
5.1 Confine Your Dog to Safe Areas
Using crates or designated rooms while unsupervised limits your dog’s access to furniture. Make these spaces comfortable with toys, bedding, and water.
5.2 Remove Temptations
Keep shoes, cushions, and other tempting items out of reach. Regularly tidy areas where your dog tends to chew to reduce opportunities for destructive behavior.
6. Professional Help and Products to Assist
If furniture chewing persists despite your efforts, consulting a professional can provide valuable insights and support. Veterinarians and animal behaviorists can assess underlying issues such as anxiety or health problems that might be driving the behavior.
For tailored solutions and high-quality products that support behavior management and pet care, visit Hidden Brook Veterinary. They offer expert advice and items designed to help dogs stay happy and your furniture intact.
Additionally, there are specialized products like calming supplements, durable chew toys, and training aids that can make a significant difference in stopping destructive chewing.
Real-life case: One dog owner shared how their Labrador puppy, Max, destroyed several couches before they discovered the root cause was separation anxiety. Through a combination of increased exercise, crate training, and professional guidance from Hidden Brook Veterinary, Max gradually stopped chewing furniture and became a calm, well-behaved companion.